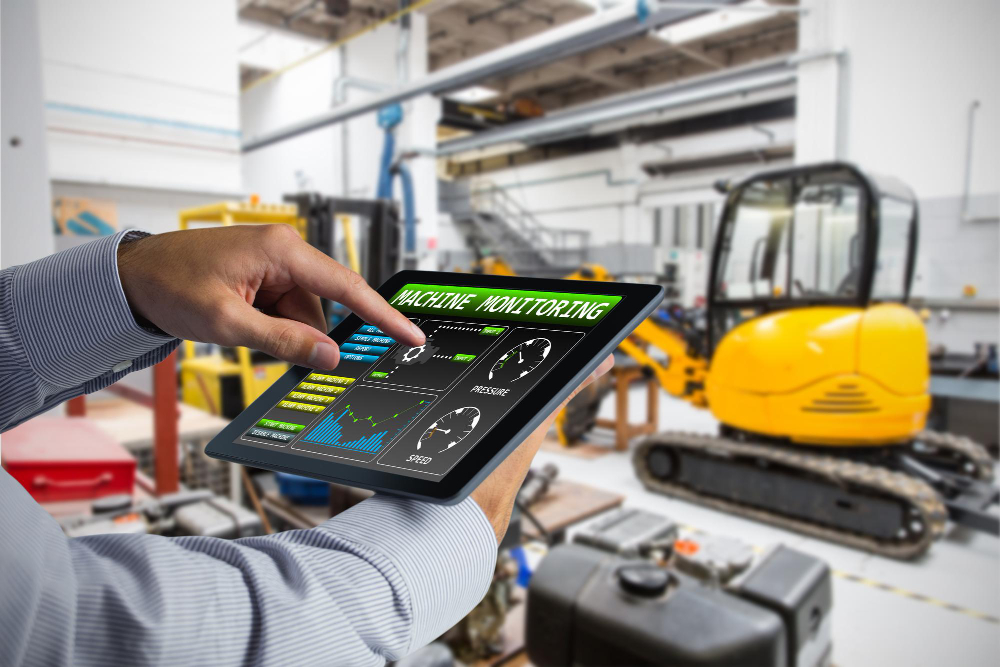
In the Industrial Automation 4.0 landscape, IIoT Controllers represent the natural evolution of traditional PLCs, integrating distributed processing capabilities with advanced connectivity features. These next-generation devices implement multi-core architectures optimized for real-time applications, simultaneously supporting the execution of deterministic tasks and the processing of advanced analytics.
Their modular architecture incorporates standardized communication protocols and open interfaces, facilitating integration with cloud platforms and legacy systems. The implementation of advanced security standards and redundancy mechanisms ensures the reliability required for critical industrial applications.
IIoT Controllers: What are Smart IIoT Controllers?
The evolution of industrial automation is converging towards the implementation of IIoT Controllers, devices that represent the beating heart of the digital transformation in the manufacturing sector. These intelligent systems integrate traditional automatic control functions with the potential of advanced connectivity and real-time data processing. Monitoring system design is a fundamental aspect of implementing these technologies, requiring a deep understanding of distributed architectures and industrial communication protocols.
The integration of smart sensors and actuators with edge computing capabilities enables the creation of highly responsive and adaptive control systems. Resource virtualization is a distinctive feature of these controllers, which implement Docker containers and microservices to ensure flexibility and scalability. The modular architecture supports the execution of machine learning and predictive analytics algorithms directly in the field, optimizing production processes through preventative maintenance and automated quality control.
Modern smart controllers are distinguished by the presence of multi-protocol interfaces that support standards such as OPC UA, MQTT, and AMQP, facilitating integration with MES systems and cloud platforms. Cybersecurity is implemented through advanced authentication mechanisms and end-to-end encryption, ensuring the protection of sensitive data and critical operations. The implementation of IEC 61131-3 languages and low-code frameworks allows for the development of complex applications with greater efficiency, while integrated web servers facilitate remote configuration and monitoring through responsive and customizable HTML5 dashboards.
IIoT Smart Controllers: The Benefits of Intelligent Monitoring in Industries
Modern industrialization is undergoing a phase of profound digital transformation, where emerging technologies are redefining traditional manufacturing paradigms. In this context of technological evolution, the integration of intelligent systems capable of orchestrating and optimizing production processes with a previously unimaginable level of sophistication is particularly important.
The convergence of industrial automation and information technology opens up innovative scenarios, where the ability to process and manage data in real time is combined with the operational efficiency of control systems. This technological synergy represents a fundamental qualitative leap in industrial process management, introducing new optimization and control possibilities that go far beyond the capabilities of traditional systems.
The digitalization of production processes requires a systemic and integrated approach, where each component must be able to communicate and interact within an interconnected ecosystem. Therefore, the advantages include:
1.Predictive Process Optimization: The implementation of IIoT controllers enables advanced analysis of production data through predictive algorithms, enabling the early identification of potential anomalies and the automatic optimization of process parameters, with an average increase in productivity of 15-20%. Intelligent 2.Energy Management: Smart monitoring systems implement energy-saving strategies through real-time consumption analysis, orchestrating machinery activation based on peak demand, and reducing energy costs by up to 30% through automated load balancing policies.
3.Advanced Preventive Maintenance: The integration of multi-parameter sensors with advanced networking solutions enables continuous monitoring of machinery status, anticipating failures through analysis of vibrations, temperatures, and operating parameters, reducing machine downtime by 45%.
4.Dynamic Production Quality: The implementation of artificial vision systems and precision sensors enables real-time quality control, with automatic corrections of process parameters and a reduction in waste of up to 35% through intelligent feedback loops.
5.Complete Supply Chain Traceability: Intelligent monitoring implements RFID tracking systems and industrial blockchain, ensuring complete traceability of materials and products, with a 60% reduction in the time to identify non-conformities.
6.Workflow Optimization: Workflow analysis through presence sensors and integrated MES systems allows for the optimization of logistics routes and operational sequences, with a 25% increase in operational efficiency. 7.Automated Environmental Management: Monitoring includes environmental sensors for controlling temperature, humidity, and air quality, with intelligent HVAC systems that automatically optimize operating conditions, reducing consumption by 40%.
8.Proactive Operational Safety: The implementation of predictive safety systems with thermal cameras and motion sensors ensures accident prevention through behavioral analysis and the identification of risky situations, reducing injuries by 65%.
9.Real-Time Inventory Management: Intelligent monitoring integrates weighing systems and volumetric scanners for automatic inventory management, optimizing orders and reducing warehouse costs by 30% through advanced just-in-time policies.
10.Automated Regulatory Compliance: The implementation of automatic reporting systems and compliance dashboards ensures continuous monitoring of regulatory parameters, with automatic generation of required documentation and a 75% reduction in audit times.
Intelligent Monitoring: Practical Applications of IIoT Controllers
In the advanced manufacturing sector, the implementation of IIoT Controllers finds practical application in the management of robotic assembly lines, where integration with vision systems and precision sensors enables real-time quality control.
The design and implementation of industrial networking supports the interconnection of autonomous production cells through Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) protocols, ensuring deterministic process synchronization with latencies of less than 1 millisecond.
The distributed architecture implements edge computing for local processing of critical data, while next-generation SCADA systems orchestrate operations through interactive web-based dashboards. Intelligent resource management then extends to micro-granular energy monitoring, enabling consumption optimization through adaptive algorithms that automatically adjust operating parameters based on actual workload.