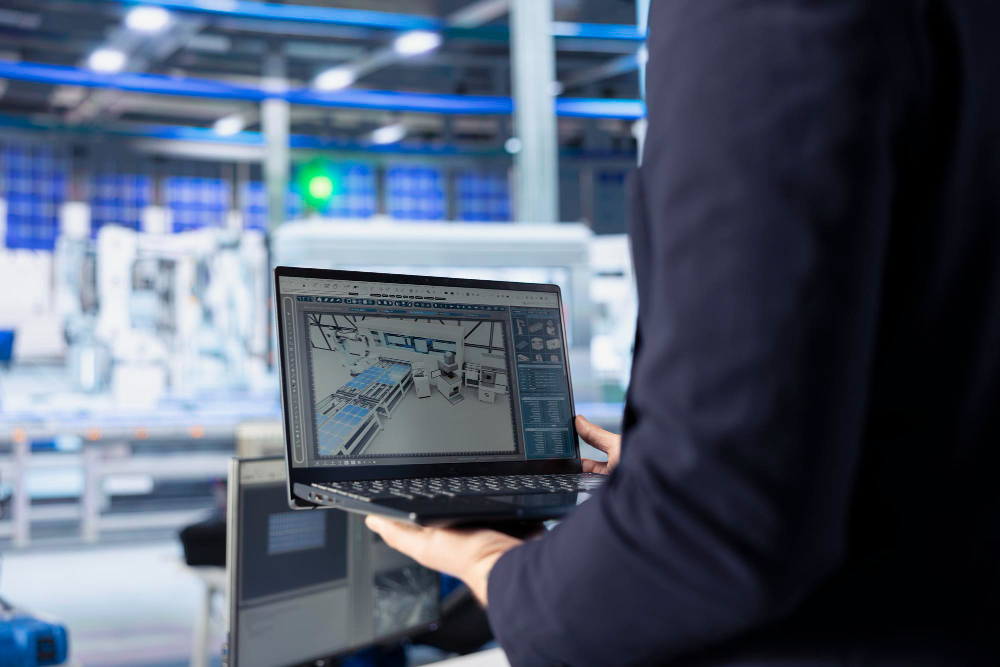
The evolution of production paradigms in the contemporary manufacturing environment requires a complete overhaul of corporate technology infrastructures. The digitalization of industrial processes is at the heart of the transformation that is redefining traditional operating models. Industry 4.0 interconnection is the foundation upon which modern automation architectures are developed, ensuring integrated information flows between machinery, management systems, and cloud platforms.
The design and implementation of industrial networking systems must meet stringent reliability and security requirements, implementing advanced communication protocols that support the transmission of critical data in real time, even in environments characterized by electromagnetic interference and harsh operating conditions.
Infrastructure Planning and Auditing
Infrastructure planning and auditing are fundamental steps in implementing advanced automation systems. The process begins with a thorough assessment of the existing infrastructure, identifying strengths and weaknesses. This preliminary analysis allows us to map all existing hardware and software resources, understanding how industrial networks are structured and interconnected. It is essential to document the current architecture, including servers, network devices, control systems, and machinery.
A comprehensive audit also examines the networks’ ability to support new workloads, evaluating parameters such as bandwidth, latency, and reliability. This phase allows us to identify potential bottlenecks that could hinder Industry 4.0 interconnection.
Strategic planning must consider current and future needs, providing scalability to accommodate business growth. It is important to establish clear metrics to evaluate infrastructure performance, continuously monitoring vital parameters such as response times, availability, and resource utilization. Automated diagnostic tools facilitate this process, offering detailed system status reports.
Planning also includes a technology roadmap that defines how the infrastructure will evolve over time, establishing priorities and timelines for investments. This roadmap aligns with business objectives, ensuring that each technological innovation effectively supports production processes.
Industry 4.0 Interconnection: Choosing Technologies and Devices
Industry 4.0 interconnection requires a careful selection of technologies and devices that form the smart factory ecosystem. The choice is based on criteria such as compatibility, reliability, scalability, and return on investment.
Key technologies include IoT sensors, SCADA systems, advanced PLCs, edge computing, and cloud platforms. These elements form the digital infrastructure that enables real-time data collection and analysis.
Sensors are the starting point, transforming physical parameters into digital data. Their selection takes into account accuracy, durability in industrial environments, energy consumption, and supported communication protocols. Temperature, pressure, vibration, and energy consumption sensors provide crucial information about production processes.
IoT gateways act as a bridge between field devices and central systems, managing data flow and converting different protocols. These devices ensure secure and reliable information transmission, often operating in critical environments.
Communication networks are the connecting element of the entire system. Technologies such as industrial Ethernet, industrial Wi-Fi, 5G, and protocols like OPC UA, MQTT, and Modbus enable data exchange between heterogeneous devices.
The choice takes into account latency, reliability, and coverage requirements.
Data management and analytics software platforms are the brains of the ecosystem. These solutions process the collected data, generating useful insights to optimize processes, predict failures, and improve quality. It is essential to select platforms with intuitive interfaces that facilitate access to information at all levels of the company.
Security, Maintenance, and Updates
Security, maintenance, and updates are critical aspects for ensuring business continuity and protecting company assets in the Industry 4.0 ecosystem. A structured approach to security includes protection measures at the physical, network, and application levels, implementing the concept of defense in depth.
Cybersecurity must be integrated from the design stage, considering that Industry 4.0 interconnectivity increases the potential attack surface.
Predictive maintenance is one of the key advantages of Industry 4.0, allowing failures to be anticipated and interventions to be planned before production downtime occurs. This approach relies on the continuous analysis of sensor data, identifying anomalous patterns that could indicate impending problems.
Software and firmware updates must be managed with particular care in industrial environments. Procedures must be established to minimize the impact on production, including scheduled maintenance windows and thorough testing before implementation in the production environment.
Continuous monitoring of operating conditions makes managing the lifecycle of company assets more efficient. Backup and disaster recovery are essential elements to ensure infrastructure resilience.
Finally, ongoing staff training is an often overlooked security measure. Operators must be aware of potential threats and security procedures, representing the first line of defense against attacks and malfunctions that could compromise the entire interconnection system.